The Apollo platform
Bring your data graph from prototype to production
The Apollo platform helps you build, query, and manage a data graph: a unified data layer that enables applications to interact with data from any combination of connected data stores and external APIs.
A data graph sits between application clients and back-end services, facilitating the flow of data between them:
An Apollo data graph uses GraphQL to define and enforce the structure of this data flow.
1. Build your graph with Apollo Server
Your data graph needs a service that processes GraphQL operations from application clients. This service communicates with back-end data sources to fetch and modify data as needed. To build this service, you can use Apollo Server.
Apollo Server is an extensible, open-source JavaScript GraphQL server. With it, you can define:
- A GraphQL schema that specifies all of the types and fields available in your graph
- A collection of resolvers that specify how to populate each field of your schema with data from your back-end data sources
You can deploy Apollo Server to any hosted or serverless environment. It supports a variety of popular Node.js middleware and works seamlessly with TypeScript.
Build incrementally
Your data graph doesn't immediately need to connect all of your back-end data sources or handle all of your client requests. The Apollo platform supports (and encourages) incremental adoption.
As you connect more data sources and expand your schema, Apollo Server can handle a larger and larger percentage of your client data requests. Clients can continue using an existing solution for requests that your data graph doesn't yet support.
Make the jump to federation
As your data graph begins to grow in size and complexity, you can use Apollo Server's extension libraries to federate your graph.
In a federated architecture, your data graph's API is implemented across multiple services instead of a monolithic server. Each service has its own GraphQL schema, and those schemas are merged by a gateway that intelligently executes operations across services.
2. Query your graph with Apollo Client
After you deploy a first version of your data graph, application clients can begin querying it. To execute these queries, you can use Apollo Client.
Apollo Client is a customizable, open-source JavaScript GraphQL client with powerful caching and state management features. It enables developers to define queries directly within the UI components that use them, and automatically update those components as query results arrive or change. It also works seamlessly with TypeScript.
Apollo Client's cache locally replicates the parts of your data graph that your client cares about. This enables your client to query itself for data if it's already present, dramatically improving performance by preventing unnecessary network requests.
Supported platforms
Apollo Client includes official support for React, and there are community-maintained libraries for other popular view layers.
Apollo Client is also officially supported on mobile with a Swift client for iOS and a Java/Kotlin one for Android.
3. Manage your graph with Apollo Studio
In addition to its open-source libraries, the Apollo platform provides a cloud-hosted collection of tools that help you measure your graph's performance and grow it safely. These tools are together known as Apollo Studio.
The schema registry
The Apollo schema registry powers many development tools, including Apollo Studio. By registering your graph's schema, you can use Studio to explore your schema's structure, track its change history, and lay the foundation for many other powerful features.
Apollo Studio features
Free for all Apollo users
-
A powerful schema explorer that helps your team build and run queries against your registered schema:
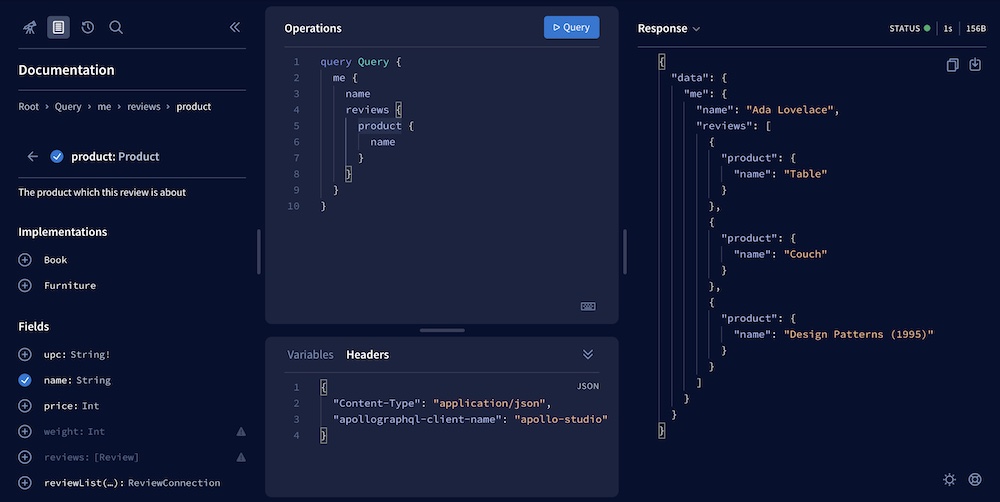
-
Metrics reporting for up to the last 24 hours:
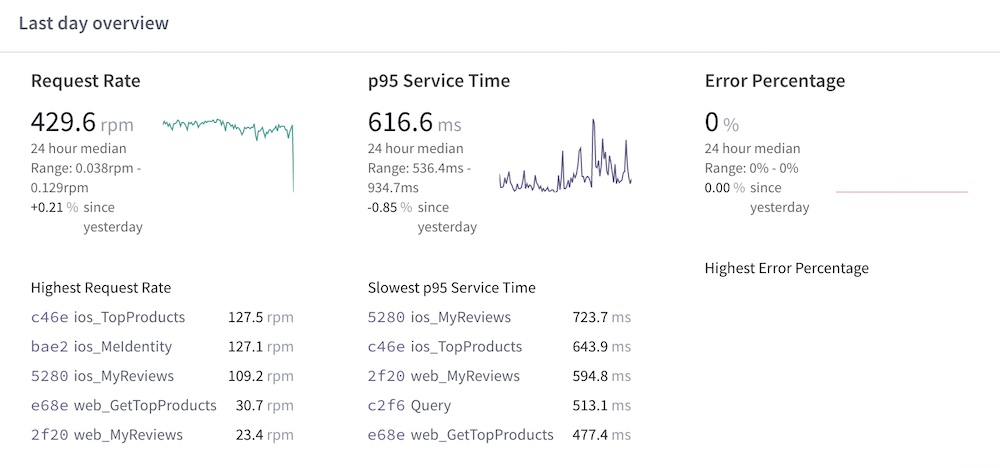
- Team collaboration via organizations
- Slack notifications for schema changes and daily metrics reports
- Management of a federated data graph
Available with an Apollo Team or Enterprise plan
- Metrics reporting for arbitrary timeframes
- Metrics segmentation by distinct clients and versions
- Schema checks
- Operation safelisting
- Resolver-level query tracing
- Integration with Datadog
- Longer data retention
4. Federate your graph with Apollo Federation
As your data graph grows, it can be useful to divide its functionality across multiple GraphQL services that own distinct portions of the graph's schema. Doing so is known as adopting a federated architecture. Apollo has defined the specification for a particular federated architecture called Apollo Federation.
We strongly recommend starting with a non-federated architecture and moving to Apollo Federation only after your non-federated graph is up and running.
Non-federated architecture
In a non-federated architecture, your monolithic GraphQL server owns the entirety of your graph's schema. When a client request comes in, the server resolves it by fetching and/or modifying data across one or more data stores that it connects to directly:
Apollo Federation architecture
With Apollo Federation, a gateway sits in front of one or more implementing services:
The gateway is a GraphQL server, and so is each implementing service. Each implementing service defines its own schema and connects to whichever data stores it needs to populate that schema's fields. The gateway then aggregates these schemas and combines them into a single schema.
When a client request comes in, the gateway knows which requested fields are owned by which service. It intelligently executes operations across whichever combination of services is needed to fully complete the operation.
Apollo Server includes extension libraries that enable it to act as either a gateway or an implementing service. And Apollo Studio provides free managed federation features that help you maximize your graph's uptime.